前言
写这篇文章的时候我甚至不会最短路,所以别骂了
1 深度优先搜索
深度优先搜索一种搜索算法,英文缩写为DFS,即Depth First Search其过程简要来说是对每一个可能的分支路径深入到不能再深入为止,而且每个节点只能访问一次。「1」
简单来说,深搜就是“一条路走到黑”。
1.1 深度优先搜索的顺序
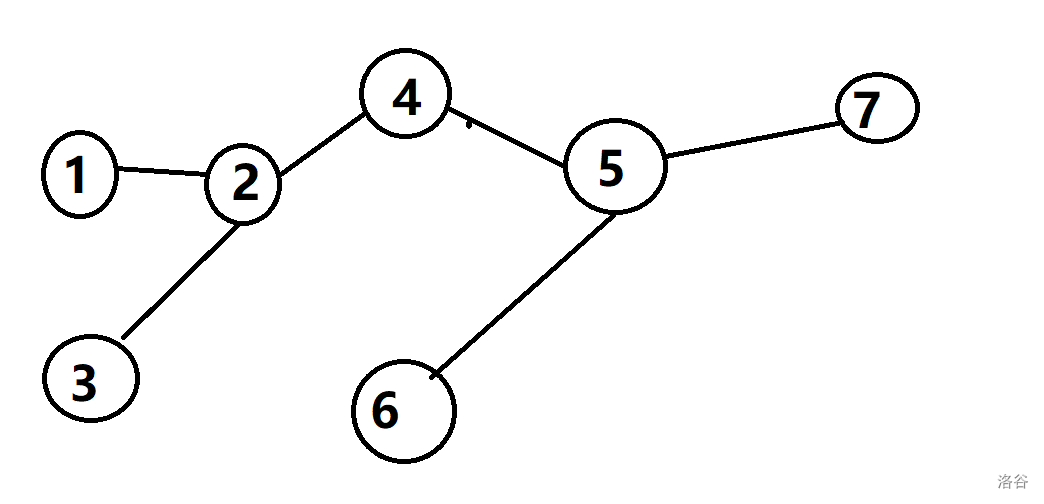
(手绘图片,有点简陋请不要介意)
步骤:
-
首先找到初始节点1。
-
依此从1未被访问的邻接点出发,对图进行深度优先遍历。
-
若有节点未被访问,则回溯到该节点,继续进行深度优先遍历。
-
直到所有与顶点1路径相通的节点都被访问过一次。
1.2 DFS模板
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
| void dfs(int v){
if() return;
for(){
if(){
dfs();
}
}
}
|
1.3 例题
洛谷P1706
全排列问题
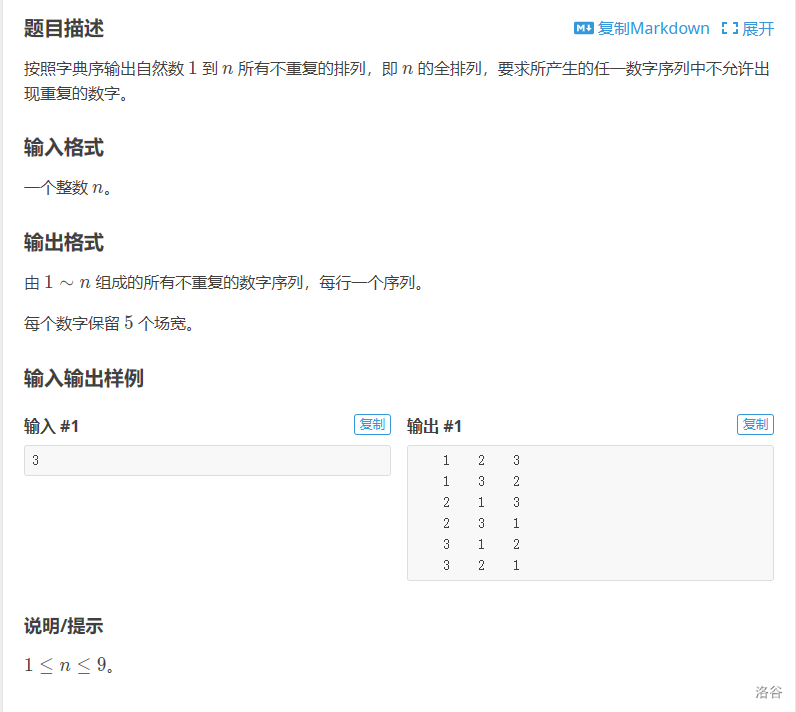
解法:
-
next_permutation函数(stl字典序全排列函数)
-
暴力枚举
-
DFS搜索
解法1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int a[10];
int main()
{
int n,i,j=1,k;
cin>>n;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{a[i]=n-i+1;j*=i;}
for(i=1;i<=j;i++)
{next_permutation(a+1,a+n+1);
for(k=1;k<=n;k++)
cout<<" "<<a[k];
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
|
解法2
暴力枚举就需要循环n次,而题目中n限定在9以内,这就需要写9个循环,但是那太多啦,所以作者就写了3个循环,代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int a=1;a<=n;a++){
for(int b=1;b<=n;b++){
for(int c=1;c<=n;c++){
if(a!=b&&b!=c&&a!=c) printf("%5d%5d%5d\n",a,b,c);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
|
解法3
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,vis[100],a[100];
void print(){
int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%5d",a[i]);
cout<<endl;
}
void dfs(int k){
if(k==n){
print();
return;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!vis[i]){
vis[i]=1;
a[k+1]=i;
dfs(k+1);
vis[i]=0;
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
dfs(0);
return 0;
}
|
时间复杂度
解法1
通过bdfs,我们知道,next_permutation函数的时间复杂度是O(n) ,再观察程序,程序内有两重循环,所以,这个程序的时间复杂度是O(n3)
解法2
暴力枚举n重循环,很明显,时间复杂度为O(nn)
解法3
n个不相同的数字的全排列有n!个,在递归的过程中,这个时间复杂度大概在O(n×n!)和O(n!)之间。
分析
所以,dfs的解法明显比暴力枚举更优。
2 广度优先搜索
广度优先搜索(Breadth First Search)简称广搜、宽搜或者 BFS。
如果说深搜是“一条路走到黑”,那么广搜就是一层一层地搜索。
那么如何实现这个过程呢?我们就需要用一个数据结构——队列。
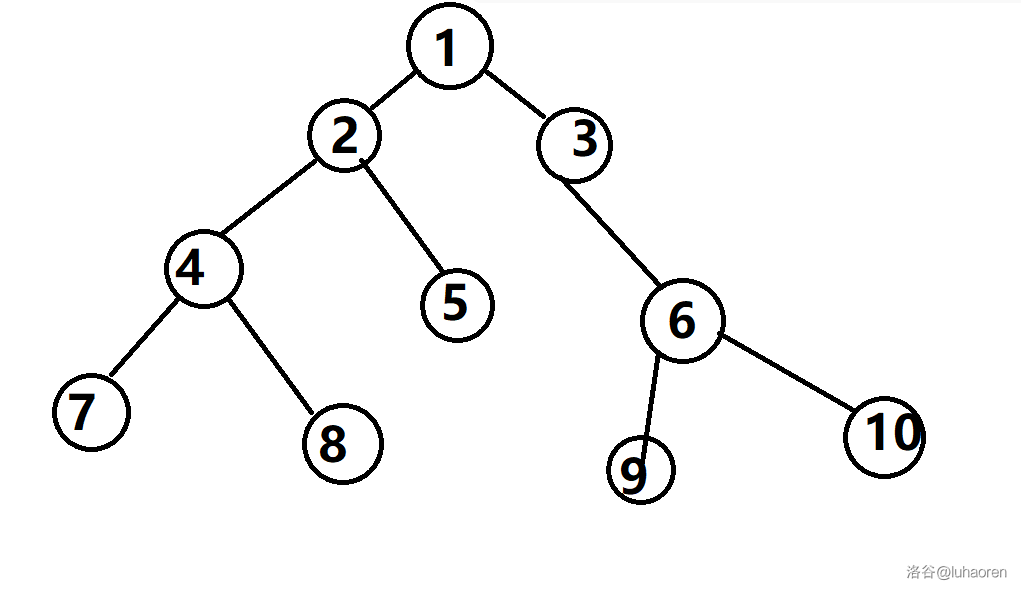
广搜的搜索顺序
-
首先找到初始节点1,把它加入队列。
-
取出队首,依此访问该节点未访问过的的邻接点,把他们加入队列。
-
重复执行步骤2,直到队列为空。
广搜模板代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| bool bfs(int v){
queue<int>q;
q.push(v);
while(!q.empty()){
int t=q.front();
if() return true;
q.pop();
for(){
if() q.push();
}
}
return false;
}
|
例题
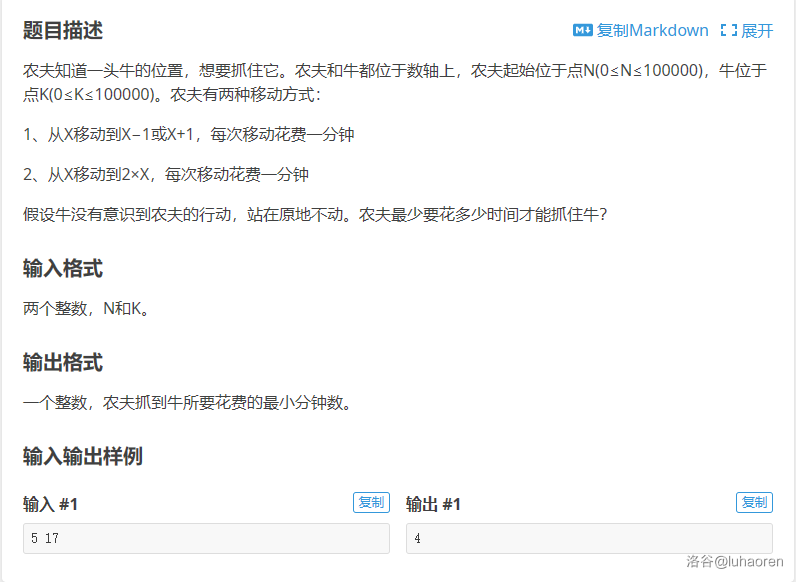
U263917 抓住拿头牛
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int,int>PLL;
const int N=100005;
int n,k;
int vis[N]={0};
int bfs(){
queue<PLL>q;
q.push({n,0});
vis[n]=1;
while(!q.empty()){
PLL head=q.front();
q.pop();
int f=head.first,s=head.second;
if(f==k) return s;
if(f+1<N&&vis[f+1]==0){
vis[f+1]=1;
q.push({f+1,s+1});
}
if(f*2<N&&vis[f*2]==0){
vis[f*2]=1;
q.push({f*2,s+1});
}
if(f-1>=0&&vis[f-1]==0){
vis[f-1]=1;
q.push({f-1,s+1});
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>k;
cout<<bfs();
}
|
3 搜索之连通性
Floodfill又名泛洪填充算法,类似于画图的油漆桶工具一样,我们把所有起点能走到的格子全部拿一个颜色标记一下,然后如果终点没有被标记就说明不能联通。
因为所有能走到的点都需要遍历一遍,并且不重复走同一个点,时间复杂度为
O(格子个数) 的。
可以BFS也可以DFS搜实现,BFS可以顺便求出来最短距离,DFS又省空间又好写,如果不求距离一般拿DFS实现。
例题#1
POJ 1818 红与黑

代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| #include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int dx[4]={1,-1,0,0},dy[4]={0,0,1,-1};
char a[110][110];
int n,m,cnt=0;
void dfs(int x,int y){
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int xx=dx[i]+x,yy=dy[i]+y;
if(a[x][y]!='#'&&x>=1&&y>=1&&x<=n&&y<=m){
cnt++;
a[xx][yy]='#';
dfs(xx,yy);
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>m>>n;
int xx,yy;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
cin>>a[i][j];
if(a[i][j]=='@') xx=i,yy=j;
}
}
dfs(xx,yy);
cout<<cnt;
return 0;
}
|




